Plan-S Installs Satellite Tracking Technology on METU’s Research Vessel
The R/V Bilim-2 research vessel, which belongs to the Middle East Technical University (METU) Institute of Marine Sciences (IMS) – one of the most established institutions in the country’s marine research – will be tracked by an IoT device developed by Plan-S. The vessel is used for oceanography, marine biology and fisheries, marine geology and geophysics, and environmental observation studies. Capable of operating uninterrupted for up to 45 days, the R/V Bilim-2 is a multidisciplinary platform equipped with advanced scientific instruments, hosting numerous research projects.
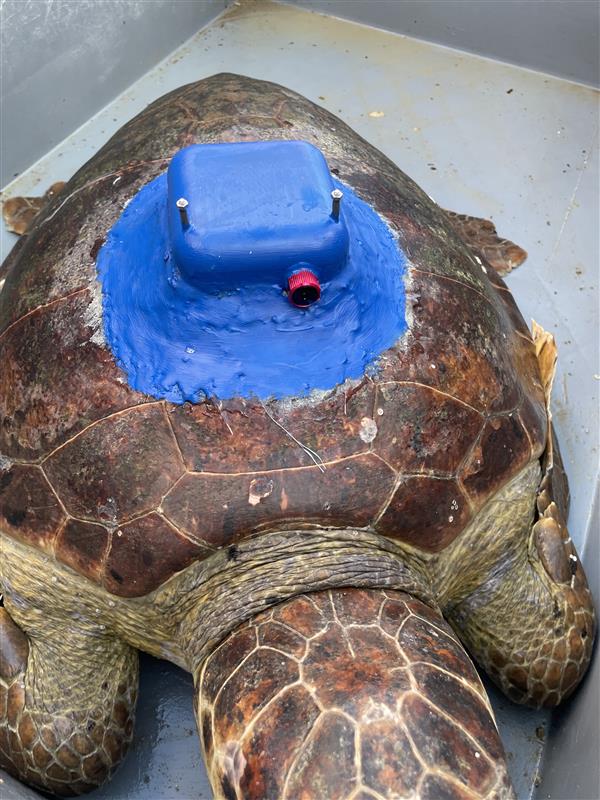
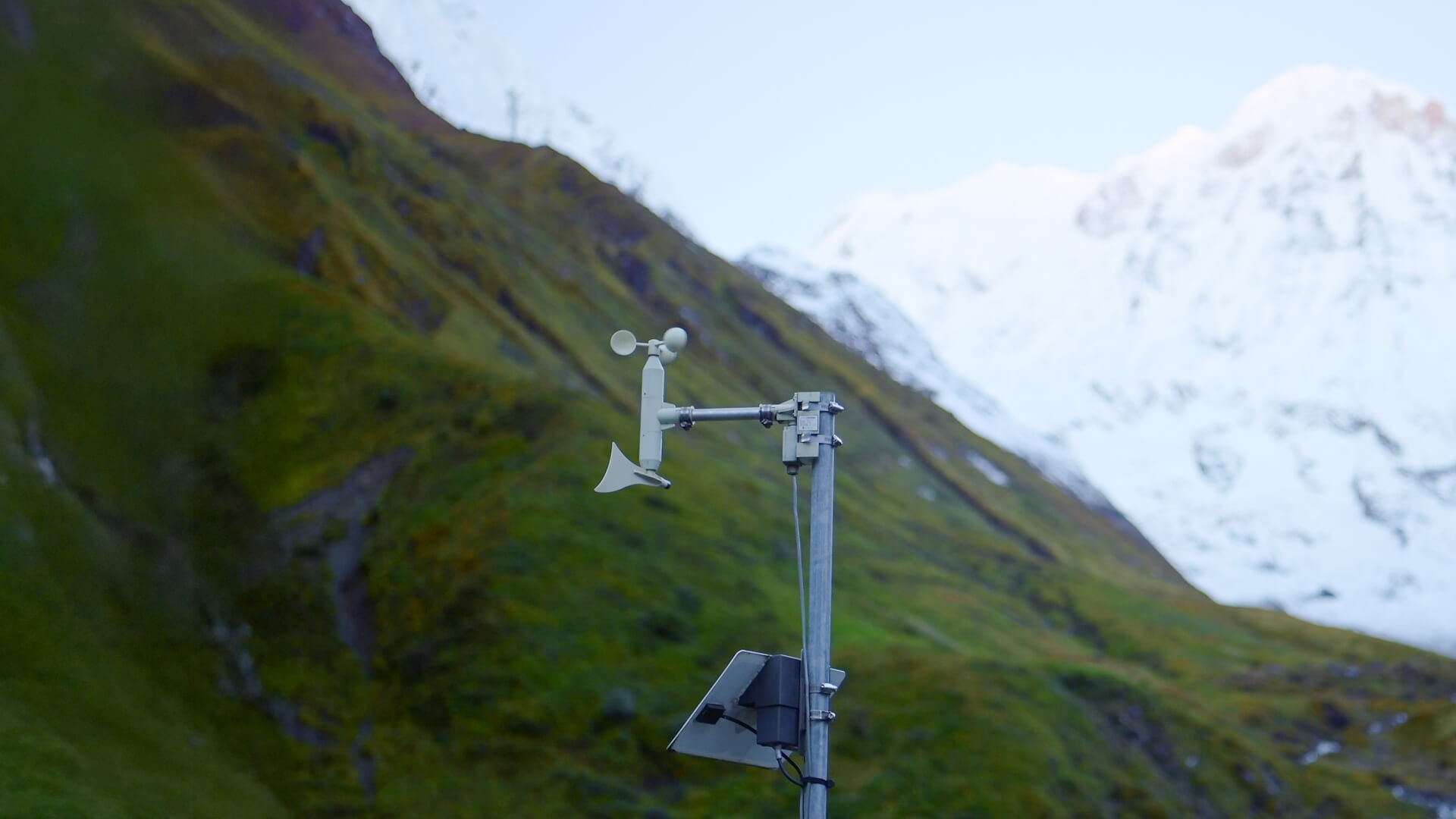
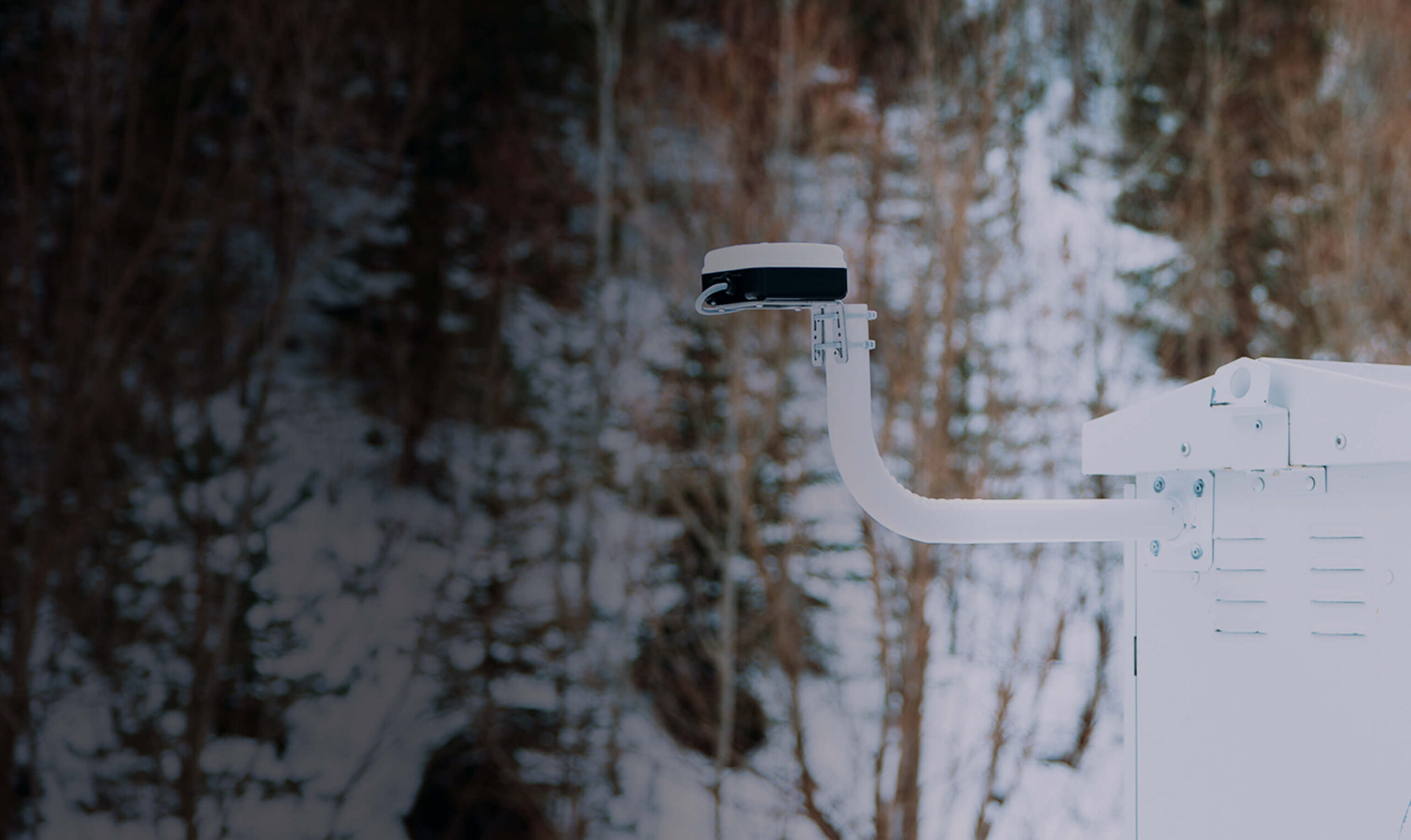
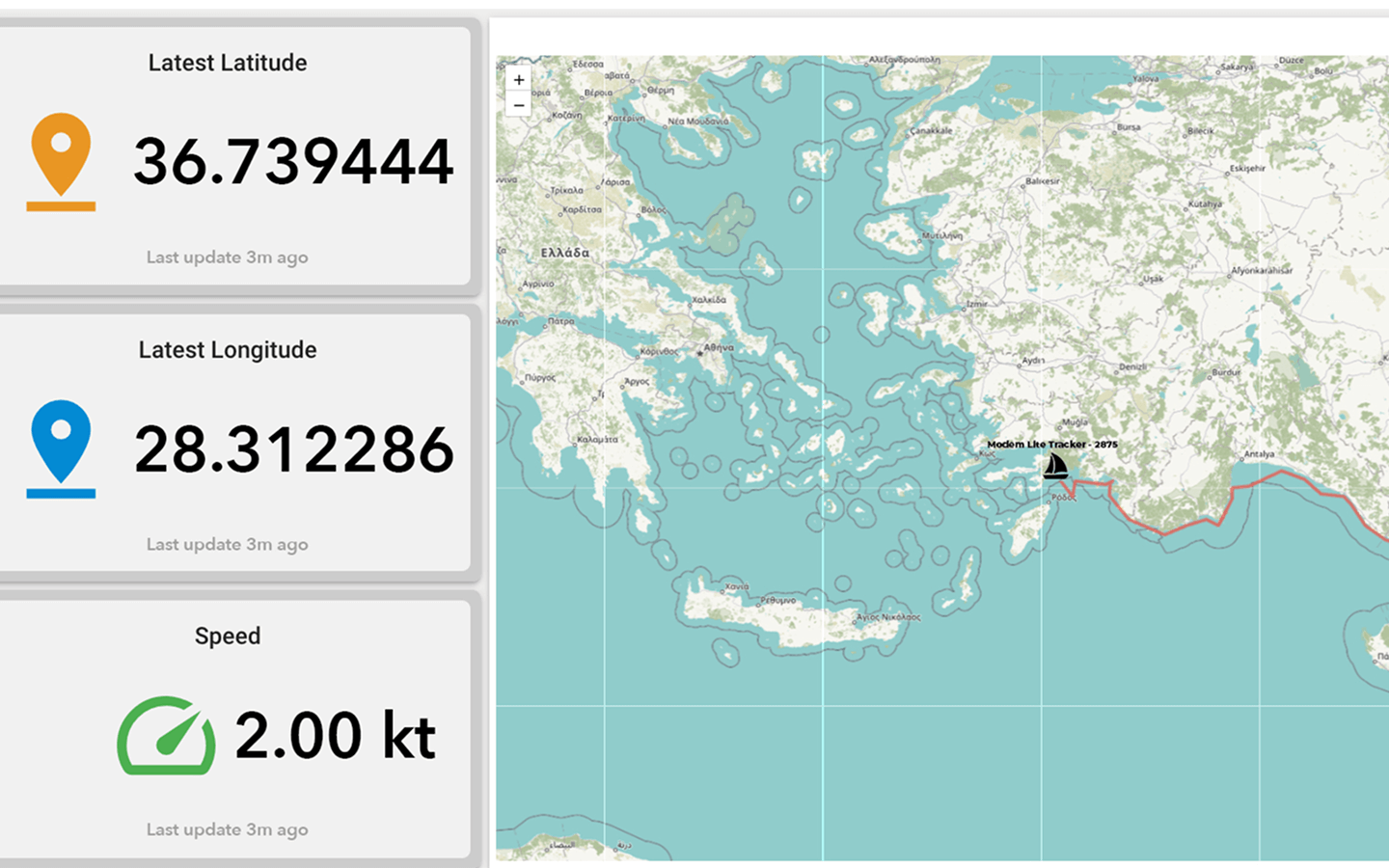
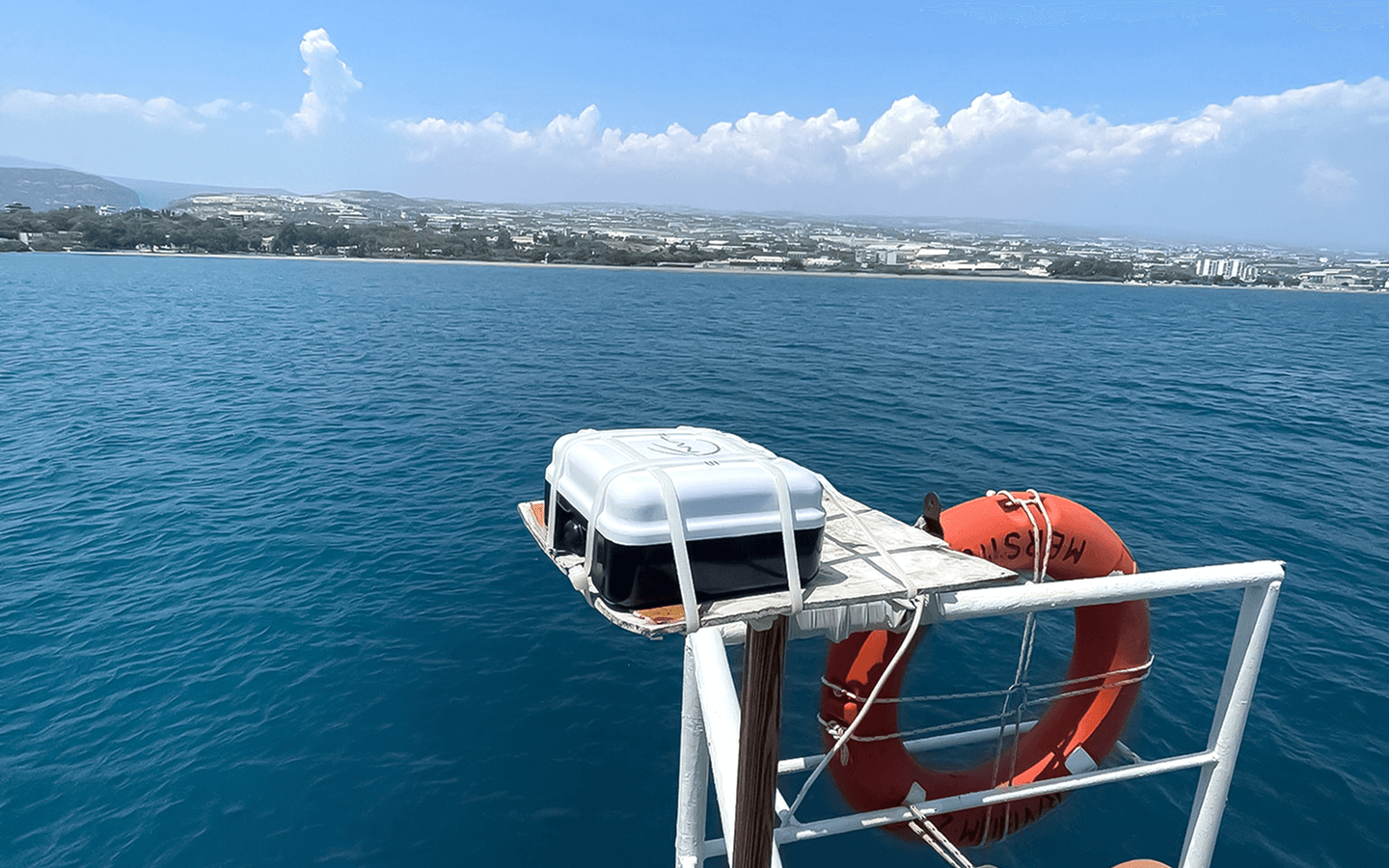
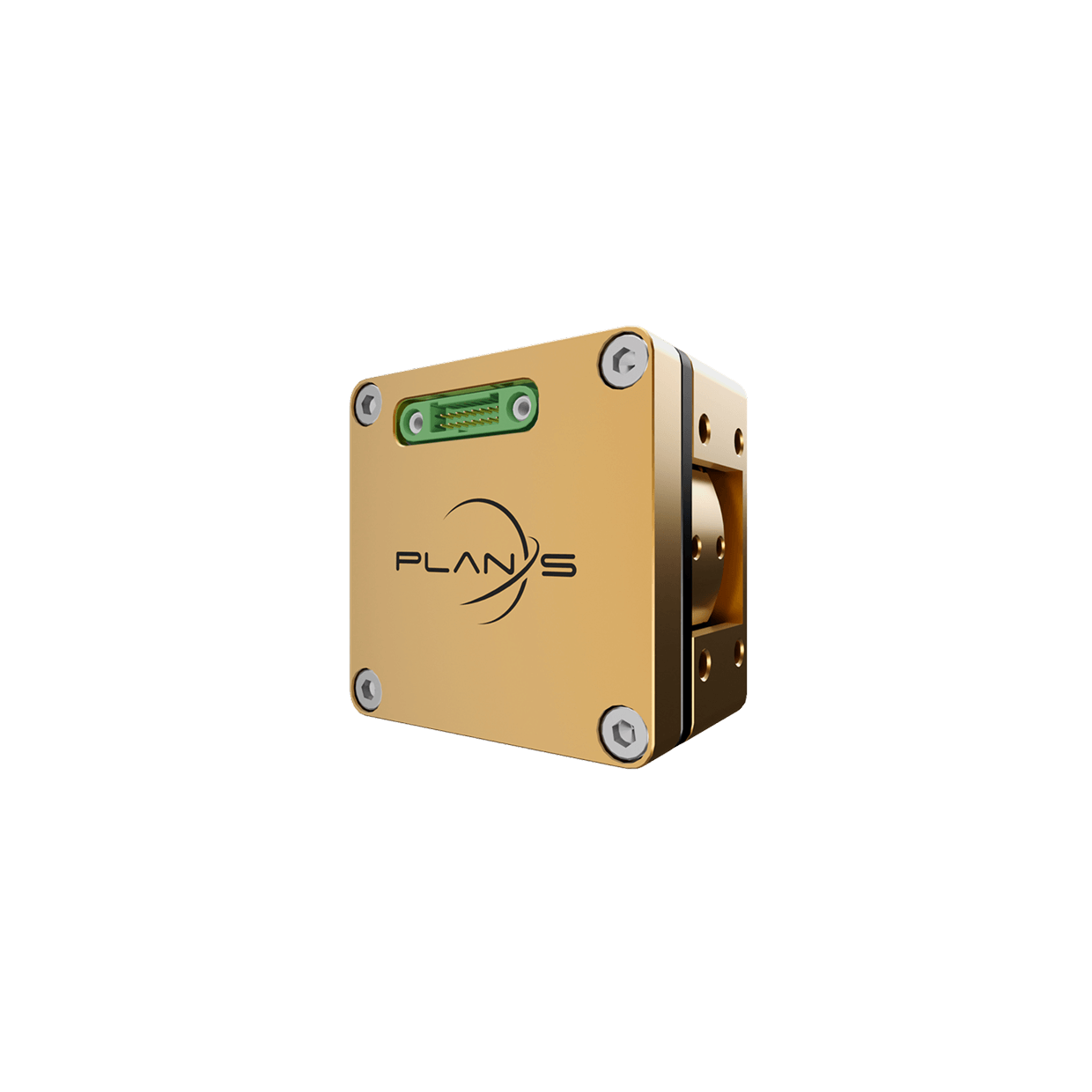
Plan-S has integrated its satellite-based asset tracking solution, the Connecta IoT Tracker Lite device, into the R/V Bilim-2, activating the satellite vessel tracking technology. The system provides uninterrupted tracking even on the high seas beyond GSM coverage. Since the beginning of August, it has been monitoring the vessel’s 45-day scientific expedition, which started from Mersin-Erdemli and covers the Mediterranean, Aegean, Marmara, and Black Seas, via satellites in orbit.
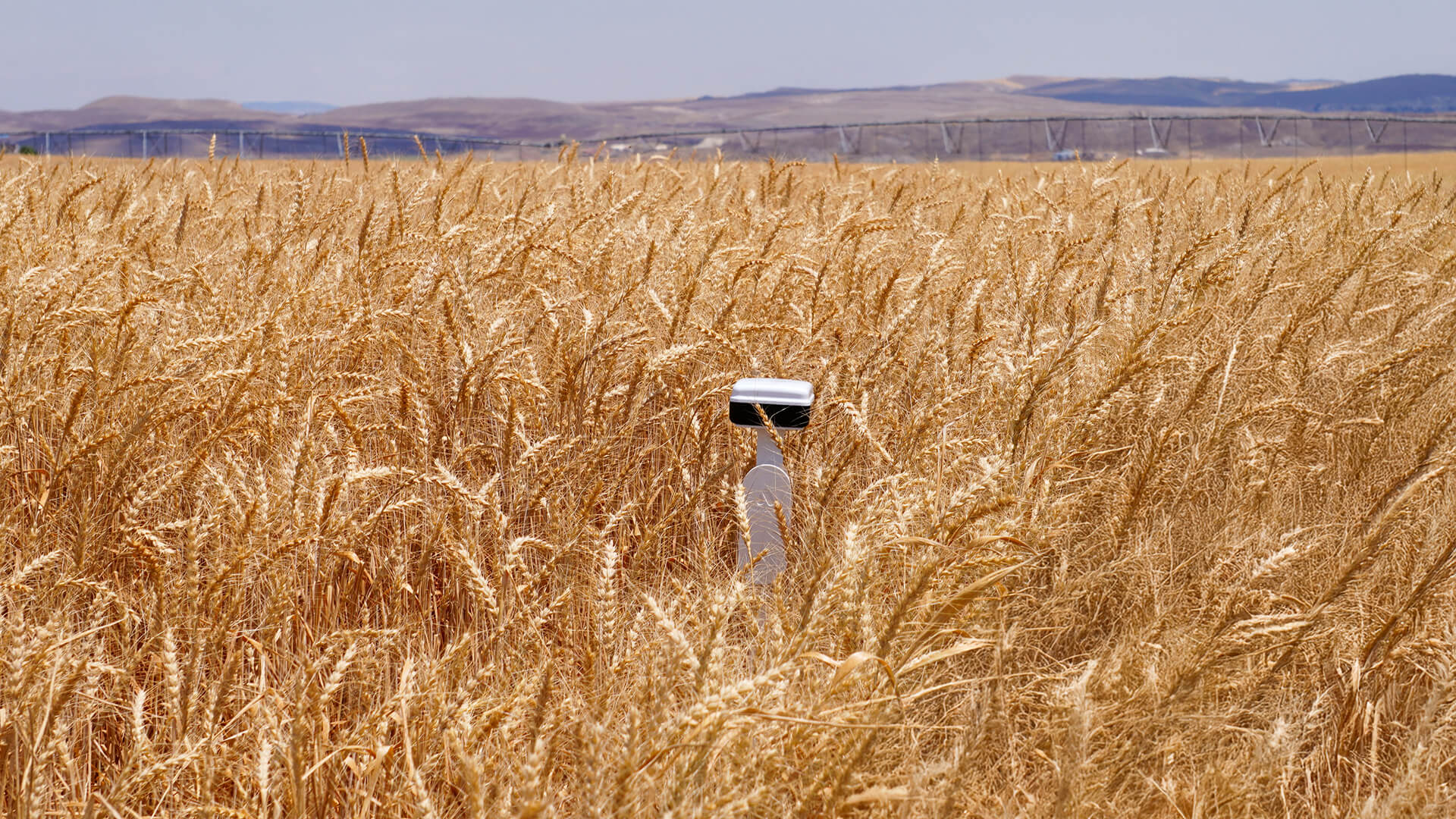
In the open ocean oceanographic observation systems developed by the METU Institute of Marine Sciences, satellite-based solutions for data transmission in areas beyond GSM coverage are critical. The constant movement of devices that track surface currents and operate autonomously creates challenges in reliably transmitting this data. Plan-S addresses this need with its satellite-based monitoring technology.
A tracker integrated into the system can transmit the device’s location data at different times to Plan-S satellites. Before deploying the technology in autonomous observation systems, METU Institute of Marine Sciences and Plan-S decided to test it on a moving platform. The device was integrated into METU’s flagship vessel, R/V Bilim-2, prior to the expedition and became operational shortly thereafter. Thus, the innovative technology for tracking moving platforms was successfully tested by enabling the research vessel to be monitored via satellites while navigating.
Satellite-Based Tracking System
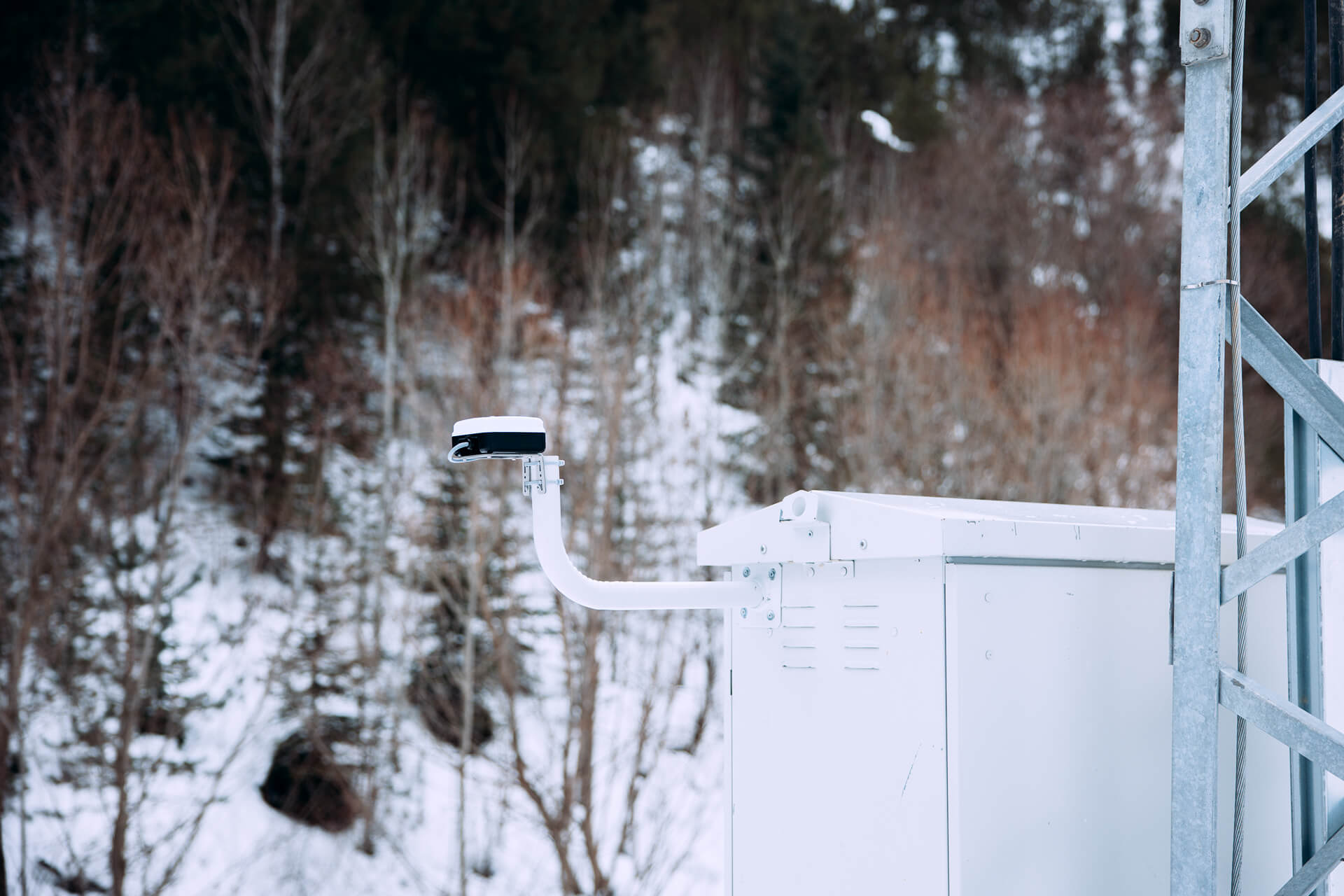
The Connecta IoT Tracker Lite activates automatically every two hours, determining and recording the vessel’s position. This data is transmitted in bulk to the METU Institute of Marine Sciences via the Connecta IoT Network during satellite passes. Plan-S aims to increase the frequency of data transmission to under 15 minutes by expanding its satellite constellation in the coming period. Thanks to its compact design, the device does not require a large mounting area and can easily be fixed to operate at any point on ships and boats with a view of the sky.
Field Durability and Reliability Tests
During the expedition, stress tests were conducted by changing the location of the Connecta IoT Tracker Lite on the vessel. The device transmitted all location data completely, providing full reliability under challenging conditions.
Scientific Contribution with Marine Observation Systems Integration
Plan-S CEO Özdemir Gümüşay stated that this collaboration would significantly contribute to oceanographic and environmental monitoring studies, saying: “This system constitutes the first step of the infrastructure that will enable data from buoys and other autonomous systems used in METU’s marine research to be transmitted via satellite, even in regions beyond GSM coverage.”
Thanks to this technology, data obtained from marine observation systems to be developed by METU can be delivered to land stations closely speed. This will not only strengthen field observation capacity but also make a significant contribution to the development of early warning mechanisms.
A Step for the Future
The Connecta IoT Tracker Lite is the first product in a series of three devices (Solar Panel, Hybrid, Modem Lite) developed by Plan-S for asset tracking. The data obtained from the R/V Bilim-2 expedition will also be used to optimize the solar and hybrid models. Thus, a significant step will have been taken towards the widespread adoption of domestic satellite-based tracking technologies in the nation’s marine research.